Sumatra Island, Originally Sumatra name originated from the existence of the Kingdom of the ocean (located on the east coast of Aceh). Starting with a visit to Ibn Battuta, a Moroccan adventure to the country in 1345, he was pronouncing the ocean becomes Samatrah, and then became Sumatra or Sumatera, then this name is listed in the maps made in the 16th century the Portuguese, to be referred to this island. Name of Sumatra, as recorded in the historical sources and folklore, is "Island of Gold". The term Ameh Island (Minangkabau language, meaning the island gold) encountered in Mato Cindua story of Minangkabau. In the folklore of Lampung listed mas Tanoh name to refer to the island of Sumatra.
Originally Sumatra name originated from the existence of the Kingdom of the ocean (located on the east coast of Aceh). Starting with a visit to Ibn Battuta, a Moroccan adventure to the country in 1345, he was pronouncing the ocean becomes Samatrah, and then became Sumatra or Sumatra, then this name is listed in the maps made in the 16th century the Portuguese, to be referred to this island, so that became known extends until now.
Name of Sumatra, as recorded in the historical sources and folklore, is "Island of Gold". The term Ameh Island (Minangkabau language, meaning the island gold) encountered in Mato Cindua story of Minangkabau. In the folklore of Lampung listed mas Tanoh name to refer to the island of Sumatra.
A traveler from China named I-Tsing (634-713), who for years lived in Sriwijaya (Palembang now) in the 7th century, called Sumatra with chin-chou name which means "golden land or Sumatra Sumatra is the sixth island The world's largest located in Indonesia, with an area of 443,065.8 km2.
The population of the island is approximately 52,210,926 (2010 census). The island is also known by another name that Percha Island, Andalas, or Suwarnadwipa (Sanskrit, meaning "golden island "). Then the inscription carved in 1286 Padang Roco swarnnabhumi (Sanskrit, meaning" land of gold ") and Bhumi Malay (" Tanah Melayu ") to refer to the island. Furthermore, in Negarakertagama manuscript from the 14th century also re-call" Earth Malay "(Malay) for this island.
In various inscriptions, Sumatra is called in Sanskrit by the term: Suwarnadwipa ("golden island") or Suwarnabhumi ("land of gold"). These names have been used in the texts of India before Christ. Buddhist manuscripts, including the oldest, the Book of J, telling Indian sailors crossed the Bay of Bengal to Suwarnabhumi. In the Ramayana story is told search Dewi Sinta, Ravana kidnapped Rama's wife, to Suwarnadwipa.
In various inscriptions, Sumatra is called in Sanskrit by the term: Suwarnadwipa ("golden island") or Suwarnabhumi ("land of gold"). These names have been used in the texts of India before Christ. Buddhist manuscripts, including the oldest, the Book of J, telling Indian sailors crossed the Bay of Bengal to Suwarnabhumi. In the Ramayana story is told search Dewi Sinta, Ravana kidnapped Rama's wife, to Suwarnadwipa.
The Arabs called Sumatra traveler by the name of "Serendib" (precisely: "Suwarandib"), a transliteration of the name Suwarnadwipa. Abu Raihan Al-Biruni, Persian geographer who visited Srivijaya in 1030, said that the country is located on the island Suwarandib Srivijaya. But there are also people who identify with Sri Lanka Serendib, who never called Suwarnadwipa.
Among the ancient Greeks, already known Sumatra Taprobana. Insula Taprobana name has been used by Klaudios Ptolemy, the Greek geographer of the second century AD, exactly 165 years, when he outlines in his Southeast Asian region Geographike Hyphegesis. Ptolemy wrote that on the island there Taprobana Barousai country. Maybe once the land is meant Barus on the west coast of Sumatra, which is well known since ancient times as a producer of camphor.
70 Greek manuscripts, Periplous Thalasses Erythras test, revealed that Taprobana also called Chryse nesos, which means 'golden island'. Since ancient times the merchants of the area around the Mediterranean Sea have come to the archipelago, especially Sumatra.
In addition to searching for gold, they look for incense (Styrax sumatrana) and camphor (Dryobalanops aromatica) who was only in Sumatra. Instead, traders archipelago was already peddling their commodities to the West Asia and East Africa, as stated in the manuscript Historia Naturalis Plini work of the first century AD.
In the book of the Jewish people, Melakim (Kings), chapter 9, explained that Solomon as king of Israel received the 420 talents of gold from Hiram, king of Tyre who became his subordinate. Gold was obtained from the land of Ophir. Kitab Al-Quran, Surah Al-Anbiya '81, explained that the ships of Solomon sailed into "the land which We have blessed him" (al-ardha l-lati-Na FIHA barracks).
Many historians are of the opinion that the country Ophir was located in Sumatra (Mount Ophir in West Pasaman, West Sumatra, which is now called Mount Talakmau). It should be noted, the city of Tyre is the central marketing of goods from the Far East. Ptolemy also wrote Geographike Hyphegesis based on information from a merchant named Marinus of Tyre. And many European travelers in the 15th century and the 16th in search of gold to Sumatra with the assumption that therein lies the land of Ophir Prophet SulaIman.
Said first mention of the name is derived from the title of a Sumatran Srivijaya king Haji (the king) Sumatrabhumi ("King of Sumatra land"), is based on the Chinese news he sent envoys to China in 1017.
Another opinion states Sumatra name is derived from the name of the ocean , the kingdom of Aceh in the 13th century and 14th century. The European travelers since the 15th century used the name of the kingdom to call the whole island. Similarly, the island of Borneo.
Borneo called, from the name of Brunei, the northern part of the island was the first visited by Europeans. Similarly, Lombok island was named Selaparang, while Lombok is the name of the area on the east coast of the island Selaparang early Portuguese sailors visited.
Transitional Ocean (royal name) into Sumatra (the name of the island) interesting to explore. Odorico da Pordenone in the story of his voyage in 1318 mentions that he sailed to the east of the Coromandel, India, for 20 days, then up at the royal Sumoltra. Ibn Batutah recalled in the book Rihlah ila l-Masyriq (Wandering to the East) that in 1345 he was stopped in the kingdom Samatrah. In the following century, the name of the country or kingdom in Aceh was taken over by the traveler-other travelers to mention the entire island.
In 1490 Ibn Majid made a map of the area around the Indian Ocean island and it said "Samatrah". Ibn Majid map was copied by Roteiro 1498 and came the name "Camatarra". Map of Amerigo Vespucci made in 1501 include the name of "Samatara", while the map Masser in 1506 gave rise to the name "Samatra". Ruy d'Araujo in 1510 call the island "Camatra", and Alfonso Albuquerque in 1512 wrote "Camatora". Antonio Pigafetta in 1521 using the name of a rather 'true': "Somatra". But so many other travelers note that more 'chaotic' wrote: "Samoterra", "Samotra", "Sumotra", even "Zamatra" and "Zamatora".
The records of the Dutch and the British, Huygen van Linschoten since Jan and Sir Francis Drake of the 16th century, has always been consistent in writing of Sumatra. Shape which is the default, and then adapted to the tongue Indonesia: Sumatera.
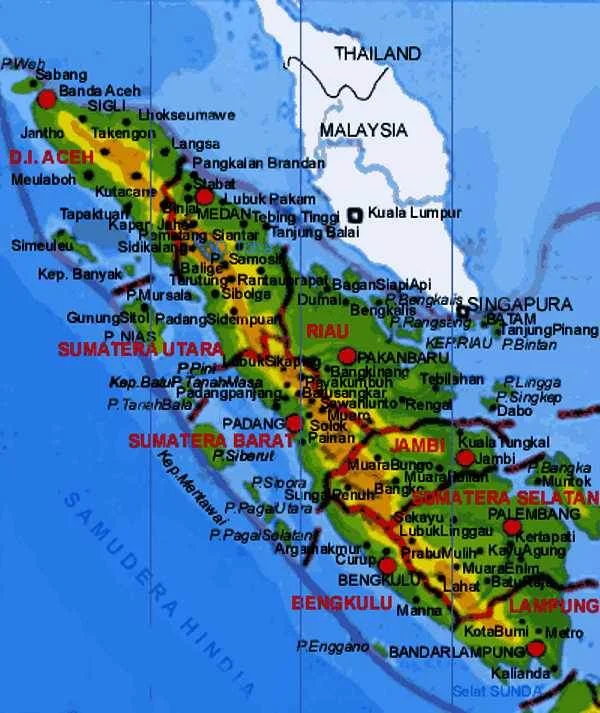
Before the expansion, in the Sumatra region there are 8 provinces namely Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam (NAD) formerly of Aceh, North Sumatra (North Sumatra), Riau, West Sumatra (boast), Jambi, South Sumatra (sumsel), Bengkulu and Lampung.
However, the current number of provinces in Sumatra and the surrounding area has been increased to 10 results from two additional new provincial division results kepulau the province of Riau (kepri) which broke away from Riau and Bangka Belitung province which broke away from South Sumatra.
Sumatra Province is divided into:
1. NAD (Nangroe Aceh Darussalam)
2. North Sumatra
3. Riau
4. Riau Islands
5. West Sumatra
6. Jambi
7. South Sumatra
8. Bangka Belitung
9. Bengkulu
10.Lampung.
In general, Sumatra island inhabited by the Malays, who are divided into several tribes. Large tribes are Acehnese, Batak, Malay, Minangkabau, Besemah, Rejang, Ogan, Ogan, and Lampung. In the eastern coastal areas of Sumatra and in some big cities such as Medan, Palembang, Pekanbaru, many ethnic Chinese living. Sumatra island residents concentrated in the East and Sumatra Minangkabau highlands. Livelihoods of Sumatra mostly as farmers, fishermen and traders.
Sumatra majority Muslim population, and a small portion are adherents of Protestant Christians, especially in the area of Tapanuli and Toba-Samosir, North Sumatra. In urban areas, such as Medan, Pekanbaru, Batam, Louth and Palembang, encountered some Buddhists.
The cities on the island of Sumatra, connected by three cross-roads, which cross the center, cross the east, and west, the cross from the northwest - southeast Sumatra. There are also roads that ran from the west - east, such as roads Bengkulu - Palembang, Padang - Jambi and Padang - Dumai.
In some parts of the island of Sumatra, the railway is an alternative means of transportation. In the southern part, the railway line starts from the port of Long (Lampung) to Lubuk Linggau and Palembang (South Sumatra).
In the middle of the island of Sumatra, the railway line is only found in West Sumatra. This path connects the city of Padang with Rice Lunto and Padang to Pariaman. During the colonial Dutch until 2001, Padang track - Rice Lunto used to transport coal. But since coal reserves in Ombilin thinning, then this path is not functioning anymore. Since late 2006, the government of West Sumatra province, re-activate this pathway as a tourist train line.
In northern Sumatra, the railway line runs from the city of Medan to High Cliff city. On this track, the train is used as a means of transporting oil palm and passengers.
International flights are served :
Banda Aceh (Sultan Iskandar Muda International Airport),
Medan (Polonia International Airport),
Padang (Minangkabau International Airport), and
Palembang (Sultan Mahmud Badaruddin II International Airport).
While the ship is in port of Belawan (Medan ),
Teluk Bayur (Padang), and
Bakauheni (Lampung).
Sumatra Island is an island rich with crops. Of the five wealthy provinces in Indonesia, there are three provinces on the island of Sumatra, which is the province of Aceh, Riau and South Sumatra. The main results of Sumatra island is palm oil, tobacco, petroleum, tin, bauxite, coal and natural gas. The results of the earth are mostly processed by foreign companies, such as PT Caltex petroleum processing in Riau province.
Places producing minerals in Sumatra:
Arun (NAD), produces natural gas.
Pangkalan Brandan (North Sumatra), produce petroleum
Duri, Dumai, and Bengkalis (Riau), produce petroleum
Tanjung Enim (South Sumatra), produces coal
Plaju and Gerong River (South Sumatra), produce petroleum
Tanjung Pinang (Riau Islands), produces bauxite
Indarung (West Sumatra), produces cement
Sawahlunto (West Sumatra), produces coal
Some cities on the island of Sumatra, is also a fairly important commercial city. Field is the largest city on the island of Sumatra, is the main commercial city on the island. Many large companies nationwide headquartered here.